Case Study
Patient J,
Male, Canadian
Table of Contents
Patient Overview
Age at time of treatment: 36 – 45
Injury Level: C6
Treatment Received: Stem Cells, Epidural Stimulation
Location of Treatment: Thailand
Time between injury and treatment: < 1 year
Date of Surgery: 16/09/2018
Date of Discharge: 02/11/2018
Condition on Admission
Patient sustained a traumatic spinal cord injury at C6 level on February 14, 2018. Patient has limited arm and hand function, but no finger function. He suffers mild spasms and spasticity, but no neuropathic pain. He requires assistance in his daily activities.
Previous Therapies & Treatments
N/A
Patient sustained a traumatic spinal cord injury at C6 level on February 14, 2018. Patient has limited arm and hand function, but no finger function. He suffers mild spasms and spasticity, but no neuropathic pain. He requires assistance in his daily activities.
Verita Neuro Treatment Received
After a spinal MRI scan, EMG, and comprehensive blood work, patient underwent laminectomy and implantation of the epidural stimulation device on September 16, 2018. The device is the ‘Medtronic Restore Advance 16-electrode MRI Compatible Device’. The surgery was completed without significant adverse events and no serious complications were reported during the postoperative hospital stay. Surgical wounds healed normally and no spinal cord or superficial wound infection was reported.
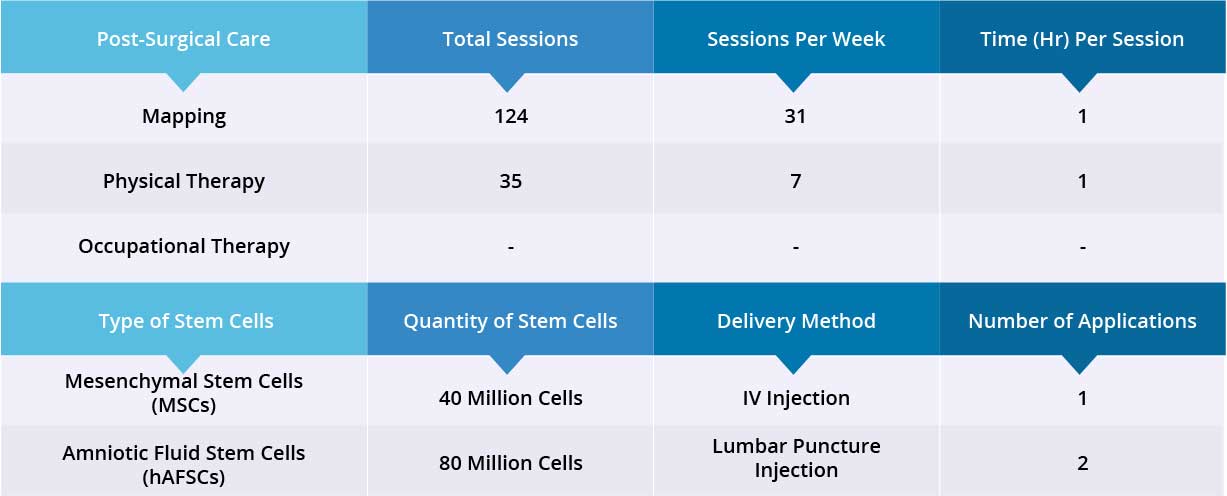
After epidural stimulation surgery, patient received 124 mapping sessions and 35 physical therapy sessions. Patient also received 120 million Stem Cells: 40 million Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) and 80 million Amniotic Fluid Stem Cells (hAFSCs) through one IV injection and two lumbar puncture injections, respectively. All three applications went well without adverse effects and no short-term or acute complications have been reported.
Device mapping and therapy were carried out after surgery for 35 days, then the patient was discharged.
Results
- Motor Functions
- Sensory Functions
- Autonomic Functions
While standing, patient has good upper trunk control, but limited lower trunk control. He applies more weight to his right leg than left leg. He is able to lock his left knee consistently, but right knee only sometimes.
Patient is able to take steps with a walking frame, no hoist required, and is able to lift both feet when taking steps. He has very good coordination between left and right foot when taking steps. Patient does not require assistance with foot placement when taking short steps, but does when taking longer steps.
Patient’s gross motor skills have improved significantly, particularly ankle, hip, and knee flexion, and knee extension (kicking out) when epidural stimulation device is switched on. Patient has good static sitting balance and no support is needed. However, during dynamic sitting, balance is poor due to weak lower trunk muscles. Static standing balance is good at the parallel bar.
Muscle mass and endurance were improved upon discharge.
In terms of Orthostatic Hypotension, patient’s blood pressure used to drop when changing positions from sitting to standing, which affected his ability to participate in physical therapy. However, with Program C on the Epidural Stimulation device, patient’s blood pressure was stable when changing positions, allowing for his therapy sessions as scheduled.
There was no noticeable improvement to his neurogenic bladder and bowel.
Patient received stem cell injections, therefore we expect to see results in these areas within 6 months time. After 35 days, patient was discharged and will continue physiotherapy back home.
During mapping sessions, patient was put on a bowel program. It helped reduce the amount of time the patient spends emptying his bowel, from 60 minutes to 30-45 minutes daily, a significant improvement in quality of life.
In terms of orthostatic hypotension, patient’s blood pressure used to drop when changing positions from sitting to standing, which affected his ability to participate in physical therapy. However, with Program C on the Epidural Stimulation device, patient’s blood pressure was stable when changing positions, allowing for his therapy sessions as scheduled.
There was no noticeable improvement to his neurogenic bladder and bowel.
Patient received stem cell injections, therefore we expect to see results in these areas within 6 months.
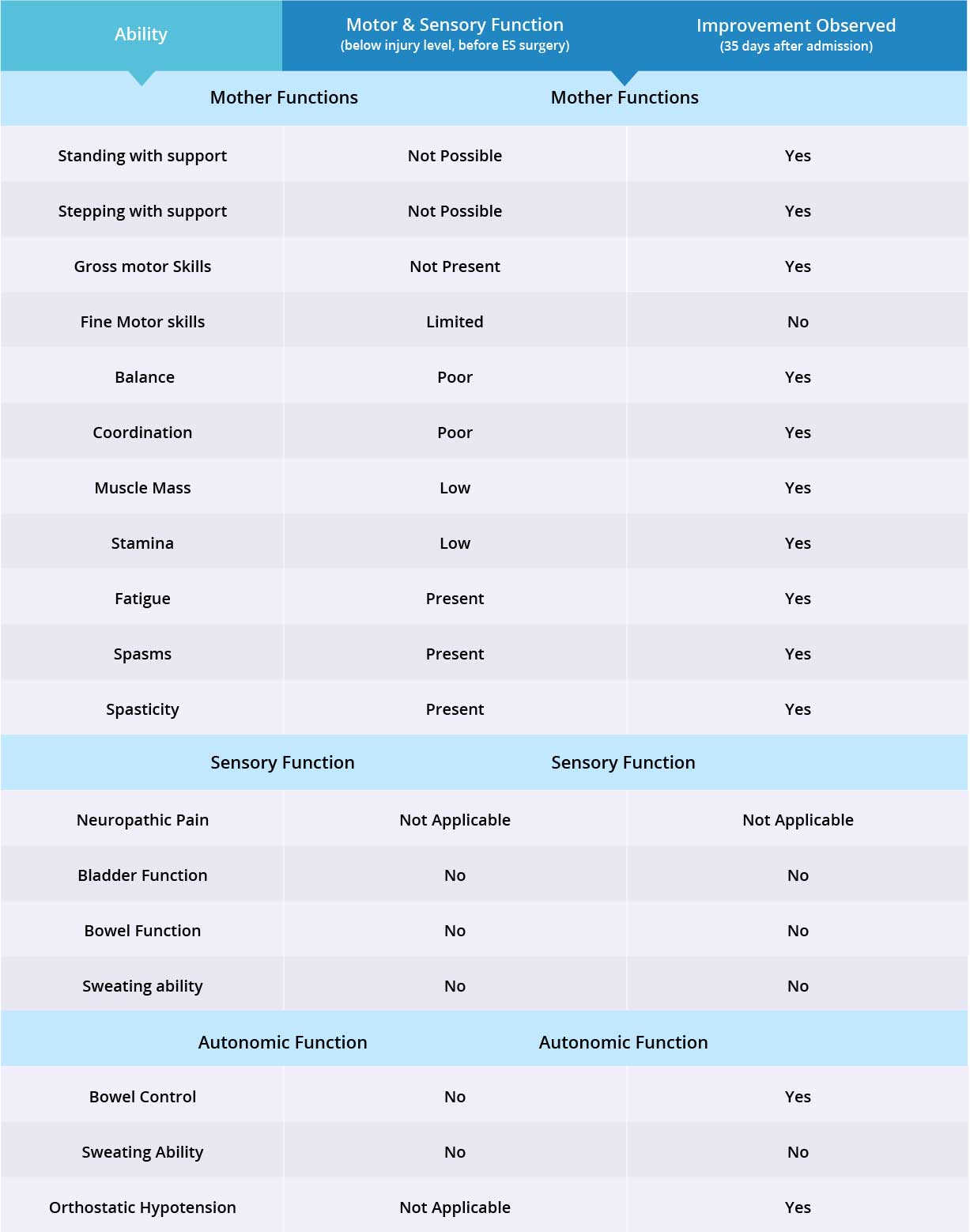
Improvements are monitored in 15 targeted areas: 11 Motor areas and 4 Sensory areas. However, the number of targeted areas may vary depending on patient’s condition prior to admission. If patient does not experience symptoms in certain Motor/Sensory functions, or is not impaired in a specific targeted area prior to surgery, it is excluded from the report (Not Applicable). If there is progress in any given area — either mild, moderate, or significant — it is measured and reported as positive (“Yes”). No improvement, the existence of pain or spasms, or an inability to perform a measured function is reported as “No”.
Results Interpretation
Motor function improved in 10 out of 11 targeted areas when the epidural stimulation device was switched on.
Patient does not suffer from neuropathic pain, therefore only 2 out of 3 sensory function areas were measured. Patient has not experienced any changes in those two sensory function areas, but more feedback will be collected after 3 months to note any improvements made by stem cell treatment.
Patient’s bowel control improved and his blood pressure increased to normal levels when the epidural stimulation device was switched on. Therefore, 2 out of 3 autonomic functions have improved. Overall, improvements were recorded in 12 out of 16 targeted motor, sensory and autonomic function areas.
